Blood sugar refers to glucose dissolved in the blood and is an important source of energy required by the human body to maintain normal physiological functions.
Stabilization of blood sugar levels is vital to good health.


Normal blood sugar levels
The normal blood sugar level range is usually 70-100 mg/dL on an empty stomach and may increase slightly to no more than 140 mg/dL 1-2 hours after a meal.

When to check blood sugar
The timing of blood glucose checks includes fasting, 1-2 hours after meals, and random times.
Fasting tests can help assess basal blood sugar levels, postprandial tests can reveal the impact of diet on blood sugar, and random tests can provide more complete information.
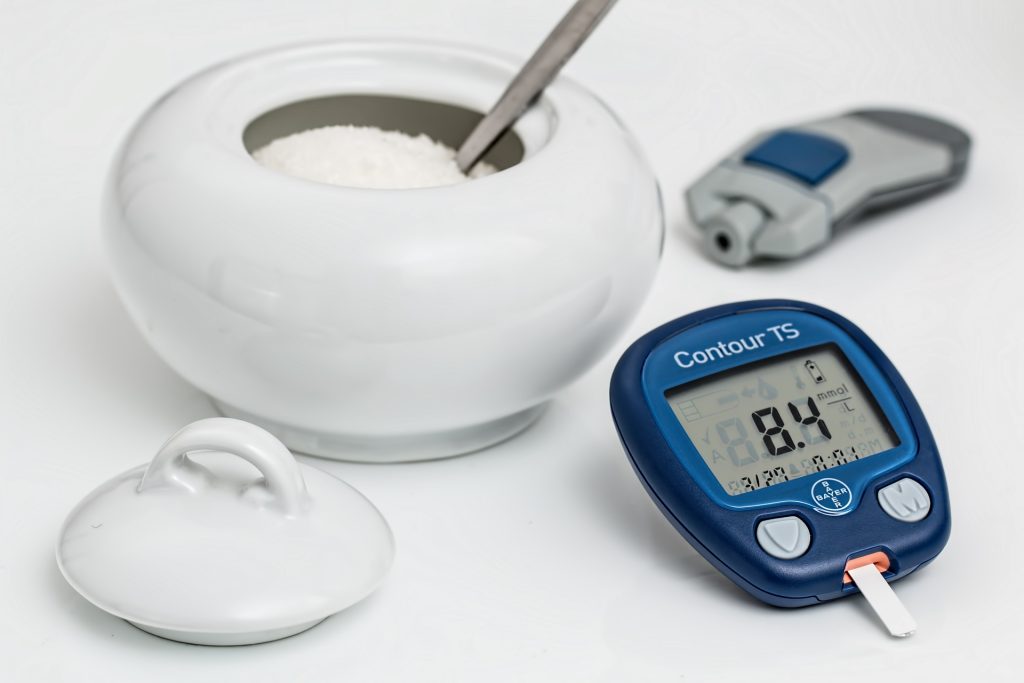
The glycemic index is an indicator of how quickly and how much the carbohydrates in food cause blood sugar to rise during digestion.
Foods with a low glycemic index can maintain blood sugar levels more stably and are beneficial to health.
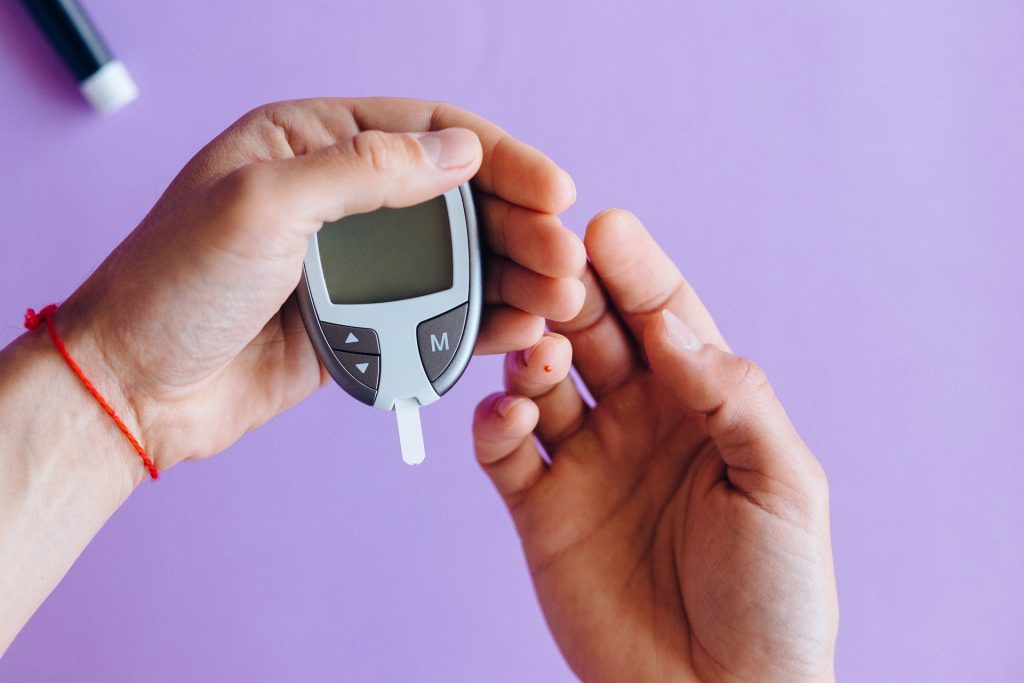
Blood glucose testing methods mainly include fasting blood glucose testing, oral glucose tolerance test, random blood glucose testing and glycosylated hemoglobin testing.
Different testing methods provide different levels of information, and doctors will choose the appropriate testing method according to their needs.
Long-term unstable blood sugar levels are potentially harmful to various systems in the body.
Can cause a variety of health problems, including:
Regular physical exercise
Moderate aerobic exercise can improve insulin sensitivity and help lower blood sugar levels.
Maintain a healthy weight
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the burden on insulin and helps prevent high blood sugar.
Reasonable dietary control
Choose foods with a low glycemic index and avoid excessive intake of foods high in sugar and fat.
Split meals
Breaking your meals into smaller portions helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Adequate water intake
Adequate water intake helps promote blood circulation and helps the body use glucose effectively.
Reduce stress
Chronic stress can cause blood sugar to rise. Employing relaxation techniques can help reduce stress levels.
Quit smoking and limit alcohol
Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake can help maintain good blood sugar levels.
Monitor blood sugar regularly
Monitoring blood sugar regularly can help detect problems early and take appropriate measures.
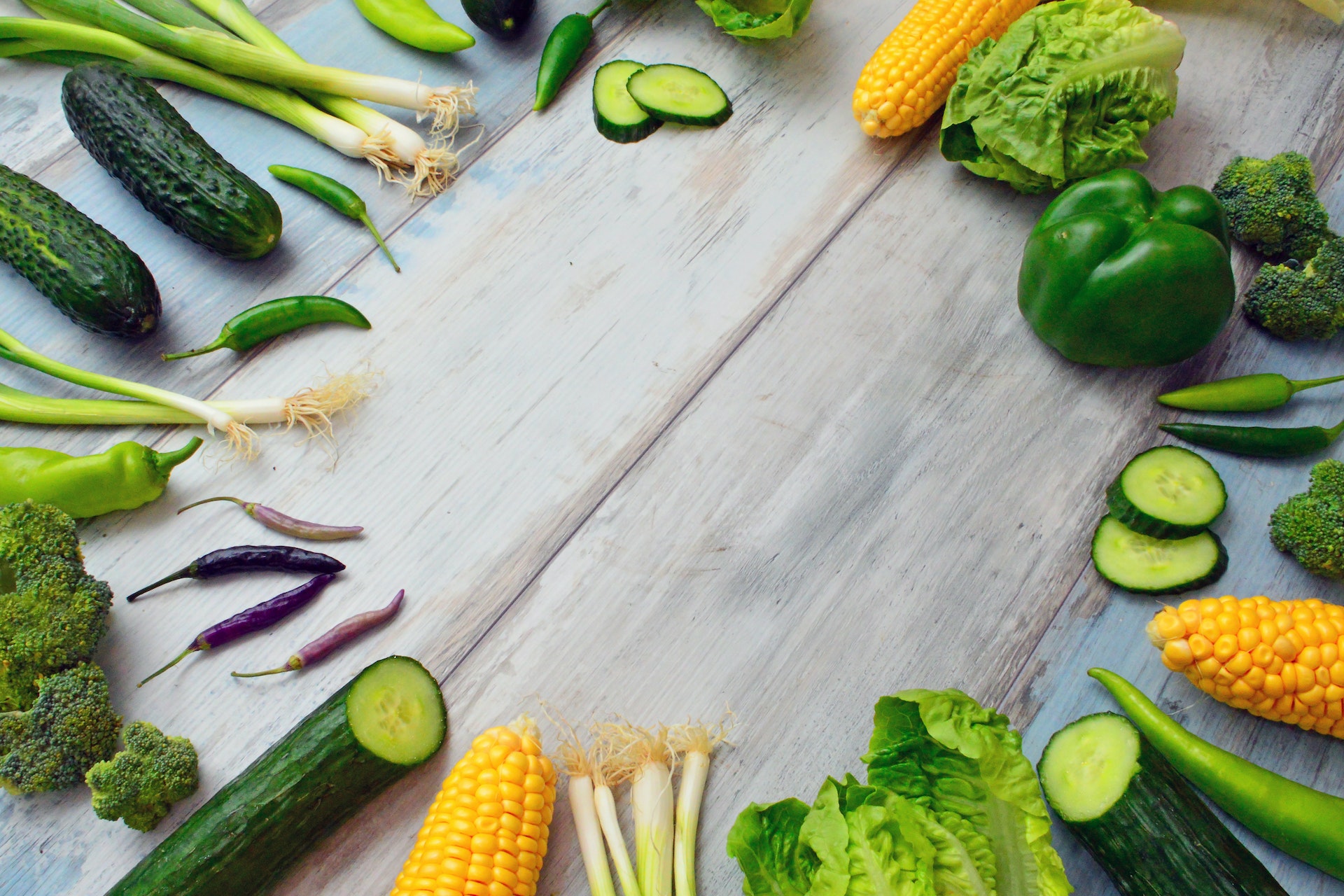

Choose low-glycemic index foods
Including whole grains (oats, brown rice, etc.), vegetables, fruits, legumes, and nuts.

Keep carbs in check
Choose complex carbs like whole grains instead of relying too much on fast-digesting carbs.

Control meal portions
Avoid taking in large amounts of food and avoid overeating.
Increase vegetables and fruits
Vegetables and fruits are rich in fiber, vitamins and minerals, and also contain natural sugars.

Control your fat intake
Choose healthy fat sources like olive oil, fish oil, nuts and avocados.

Moderate amounts of protein
Choose lean meats, poultry, fish, beans and low-fat dairy products as good sources of protein.

Control your salt intake
Choose foods with little or no added salt and use more herbs and spices for seasoning.